Bohr's Atomic Model
Neils Bohr in 1913 gives a simple model for atomic structure based on the quantum theory.
Main assumption of Bohr atomic model-
1. All atoms consist of dense, very small, positively charged nucleus that have all protons and neutrons in it.
2. Electron revolve around nucleus in definite energy paths known as orbits, shell or energy levels.
3. Orbits denoted by (n). value of n is whole number 1,2,3,4.......... etc. which are represented as K,L,M,N............. etc. respectively.
 |
| Bohr Atomic Model |
4. As we increase the value of n the orbit move farther from nucleus (means distance between nucleus and orbit of higher n is more than smaller n) and their energy also increases so n=1 or K shell have lowest energy.
5. If an electron revolve in same energy level then their is no change in its energy level.
6. As electron absorb energy from outside, it gets exited and move to
higher energy level and come back after emitting energy to lower energy
level.
 | |
| Absorption and Emission of Electron Energy |
Bohr’s model for hydrogen atom
=> Explain
by nails Bohr (1913).
=> Postulates
for Bohr’s modal are,
1. Electron
in hydrogen atom move around nucleus in circular path of fixed radius and energy.
these paths are called orbits
2. Energy
of e does not change with time.
However, when electron move from
lower to higher stationary state it absorbed sub amount of energy and energy
release when it comes back.
3. Frequency
of radiations emitted or absorbed when transition of e occur is given by
Limitation of Bohr’s model:-
1. Bohr
model fail to explain finer detail of hydrogen atom spectrum observed by spectroscopic,
techniques.
2. It
fails to explain spectrum of other atom except hydrogen atom.
3. It
fails to explain splitting of the spectral lines in presence of electric (stark
effect) or magnetic field ( Zeeman effect )
4. Fell
to explain formation of molecules from atoms by chemical bonding.
By- Chemistry Notes Info @ www.chemistrynotesinfo.com
Prepared by Jitendra Singh Sandhu
M.Sc. Chemistry

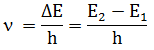

%20(1).png)
