Periodic Trends In Physical Properties
1. Atomic Radius :-
·
“Atomic radius decreases with increases
in atomic no. in a period” because within the period, the outermost electrons
are within the same valence shell. Also effective nuclear charge increases with increase in
atomic no. results in increased attraction force between nucleus and outer electrons
.
·
“Atomic radius increases with increase
in atomic no. in a group” because of filling of inner orbital’s with electrons
which serve to shield the outer electron from the attraction of nucleus, so
size of atom increases.
2. Ionic Radius :-
On general, the trend of ionic radius is same as that of atomic radius.
·
In ions lose of gain of electron takes
place while no charge in nuclear charge.
·
Size of cation (A+) is
smaller than its parent atom due to loss of electron.
·
Size of anion (A-) is large
than its parent atom due to gain of electron.
3. Ionization Enthalpy :-
Quantitative measure of tendency of an element to loose electron is known as ionization enthalpy.
·
Ionization enthalpy is always +ve.
·
2nd ionization enthalpy is
higher than 1st ionization enthalpy.
·
Alkali metals have lowest and noble
gases have highest ionization energy.
·
Ionization enthalpy increases on going
left to right in a period.
·
And decreases on Moring downwards in a
group.
Ex:-
4. Electron Gain Enthalpy :-
When an electron is added to a neutral gaseous atom to convert it into a - ve ion, the change in enthalpy in the process is given by electron gain enthalpy.
Ex:-
It may be exothermic or endothermic
reaction.
·
Halogens show exothermic reaction &
have height – ve electron gain enthalpy.
·
Noble gases show endothermic reactions
& have lowest +ve electron gain enthalpy.
5. Electronegativity: -
The qualitative measure of ability of atom to attract shared electrons from chemical compound (or chemical bond) toward itself is known as electronegativity.
·
It generally decreases down in a group and
increases in a period from left to right.


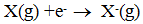
%20(1).png)
