Some Basic Concept Of Chemistry
 |
Some Basic Concept of Chemistry
|
- Basic constituents of matter: - Atoms and molecules.
- What is chemistry: - It is the branch of science which deals with the study of composition, properties and interaction of matter.
- Matter: - Anything which has mass and occupies space known as matter. Ex: - Water, pencil, pen, book etc.
Physical states of matter
Physical
state
|
Definite
volume
|
Definite
shape
|
Example
|
Solid
|
Yes
|
Yes
|
Book, pen
|
Liquid
|
Yes
|
No
|
Water, milk
|
Gas
|
No
|
No
|
CO2, Air
|
Classification of matter: -
Properties of matter
- 1) Physical properties: - Those properties which can be measured or observed.
- 2) Chemical properties: - those properties in which chemical changes occurs.
- Ex: - Acidity, Basicity, Combustibility etc.
- SI: - International System of units
- Ø SI Units are established by 11th general conference on weight and measures.
- Ø SI have seven fundamental units.
- Ø Other units are divided from seven fundamental units.
Base physical quantity
|
Symbol for quantity
|
SI units name
|
SI units symbol
|
Length
|
l
|
Metre
|
m
|
Mass
|
m
|
Kilogram
|
Kg
|
Time
|
t
|
Second
|
s
|
Current
|
I
|
Ampere
|
A
|
Temperature
|
T
|
Kelvin
|
K
|
Amount of substance
|
n
|
Mole
|
Mol
|
Luminous intensity
|
Iv
|
candela
|
Cd
|
Prefixes for SI Units
Multiple
|
Prefix
|
Symbol
|
10-24
|
Yocto
|
y
|
10-21
|
Zepto
|
z
|
10-18
|
Atto
|
a
|
10-15
|
Femto
|
f
|
10-12
|
Pico
|
p
|
10-9
|
Nano
|
n
|
10-6
|
Micro
|
m
|
10-3
|
Milli
|
m
|
10-2
|
Centi
|
c
|
10-1
|
Deci
|
d
|
10
|
Deca
|
da
|
102
|
Hecto
|
h
|
103
|
Kilo
|
k
|
106
|
Mega
|
M
|
109
|
Giga
|
G
|
1012
|
Tera
|
T
|
1015
|
Peta
|
P
|
1018
|
Exa
|
E
|
1021
|
Zeta
|
Z
|
1024
|
yotto
|
Y
|
SI Units Infographics
Laws of chemical combinations
Dalton’s Atomic Theory
Concentration expression methods
Online Video Classes of 11th Class Chemistry
Mole Concept Infographics
Lets Understand The Laws of Chemical Combinations in More Easy Ways:
1. Law of Conservation of Mass
Mass can neither be created nor destroyed in a chemical reaction.
Meaning of this law: The total mass of reactants is always equal to the total mass of products.
Example:
H2 + Cl2--> 2HCl
Total mass before reaction = total mass after reaction.
2. Law of Definite Proportions (Law of Constant Composition)
A chemical compound always contains the same elements combined in a fixed proportion by mass, irrespective of its source or method of preparation.
Example:
Water (H2O) always contains:
=> Mass ratio of H : O = 1 : 8
3. Law of Multiple Proportions
When two elements combine to form more than one compound, the masses of one element that combine with a fixed mass of the other are in simple whole-number ratios.
Example:
Carbon and oxygen form CO and CO₂.
For 12 g of carbon:
4. Law of Reciprocal Proportions
If two elements combine separately with a fixed mass of a third element, the ratio of the masses in which they combine is the same or a simple multiple of the ratio in which they combine with each other.
Example:
=> Carbon + Hydrogen → CH₄ (H = 4 g with 12 g C)
=> Carbon + Oxygen → CO₂ (O = 32 g with 12 g C)
=> Ratio H : O = 1 : 8,
=> which is the same ratio in which hydrogen and oxygen combine in water.
Importance of Learning Laws of Chemical Combinations
=> Form the basis of stoichiometry
=> Explain quantitative relationships in reactions
=> Support atomic and molecular theories
=> Essential for school chemistry, competitive exams (JEE/NEET), and laboratory calculations etc.
Law of Chemical Combinations Infographics
Some Basic Concepts of Chemistry Class 11 MCQ
1. If a matter has definite volume and definite shape, then it is :
SolidLiquid
Gas
All of the Above
2. Mole is SI unit of :
CurrentTemperature
Amount of Substance
3. A measured temperature is 100 0F on Fahrenheit scale, then what is this reading be on Celsius scale :
4. What amount of H2O produced by combustion of 32 g of CH4 :
36 g18 g
72 g
90 g
5. How many moles of CH4 is needed to get 44 gram CO2 after combustion:
0.5 mol of Methane1 mol of Methane
2 mol of Methane
4 mol of Methane


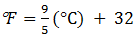






%20(1).png)
