Classification of Elements
Mendeleev periodic law :-
Mendeleev explanation that properties of the elements are periodic function of their atomic weights.Modern periodic law :-
Moseley (1913) according to this law physical & chemical properties of the elements are periodic functions of their atomic numbers.s - Block elements: -
Elements of group 1 (Alkali metals) with ns2 outermost electronic configuration.
·
These are all reactive metals with low
ionisation enthalpies.
·
They lose electrons rapidly to form +1
& +2 ions.
·
Metallic character and reactivity
increases on going down the group.
p – Block elements: -
These elements belong to group no. 13 to 18.
·
These with s – block elements are called
representative elements.
·
Outermost electronic configuration is
varies from ns2 np1 to ns2 np6.
·
Element of group 18 (ns2 np6)
are known as noble gases or invert gases.
·
Elements of group 17 known as halogens
and elements of group 16 known as chalcogens.
·
Group 16 & 17 elements have high -ve
electron in their outermost shell to attain stable inert gas configuration.
·
Non-metallic character increase on
moving left to right in period and metallic character increases on moving down
in the group.
d – Block element: -
These are elements of group no. 3 to 12 in centres of periodic table. Also known as the transition elements.
·
General outer most electronic
configuration is (n-1)d1-10 n0-2
·
These are all metals
·
Form colours ions and show variable
valences & par magnetism
·
Mainly
used as a catalyst
·
Zn , cd , Hg with configuration (n-1)d10
ns2 do not show most
of the properties of transition elements.
f– Block element: -
These have 2 – rows of elements at bottom of periodic table. i.e. lanthanides Ce (z = 58) to Lu (z = 71) Actinides Th (z = 90) to Lr (z = 103) .
·
Outer electronic configuration =(n-2) f1-14
(n-1) d0-1 ns2.
·
f – block elements also known as inner
transition elements.
Metals: -
These are more than 78% of all known elements. And present in the left side of periodic table.
·
These are usually solids at room temp.(meaning (Hg) is
exception)
·
This have high melting points .
·
Boiling point.
·
These are metallic (can be flattened
into thin sheet by hammer) and ductile
(can be drawn into winner).
Non – metals :-
These present in the top right hand side of periodic table.
·
These are usually gases or solids at
room temp. With low melting points & boiling points Boron (B) & Carbon
(C) are exception.
·
Most of non – metallic solids are brittle and
neither malleable not ductile.
·
Metallic character increases down in the
group.
·
Non – metallic character increases from
left to right in a period.
Metalloids :-
Elements which show character of both i.e. metals and non – metals are known as metalloids or semi-metals.
Ex: -
silicon, germanium, arsenic, antimony, tellurium.
Periodic trends in physical properties:-
1. Atomic radius :-
·
“Atomic radius decreases with increases
in atomic no. in a period” because within the period, the outermost electrons
are within the same valence shell. Also effective nuclear charge increases with increase in
atomic no. results in increased attraction force between nucleus and outer electrons
.
·
“Atomic radius increases with increase
in atomic no. in a group” because of filling of inner orbital’s with electrons
which serve to shield the outer electron from the attraction of nucleus, so
size of atom increases.
2. Ionic radius :-
On general, the trend of ionic radius is same as that of atomic radius.
·
In ions lose of gain of electron takes
place while no charge in nuclear charge.
·
Size of cation (A+) is
smaller than its parent atom due to loss of electron.
·
Size of anion (A-) is large
than its parent atom due to gain of electron.
3. Ionization enthalpy :-
Quantitative measure of tendency of an element to loose electron is known as ionization enthalpy.
·
Ionization enthalpy is always +ve.
·
2nd ionization enthalpy is
higher than 1st ionization enthalpy.
·
Alkali metals have lowest and noble
gases have highest ionization energy.
·
Ionization enthalpy increases on going
left to right in a period.
·
And decreases on Moring downwards in a
group.
Ex:-
4. Electron Gain enthalpy :-
When an electron is added to a neutral gaseous atom to convert it into a - ve ion, the change in enthalpy in the process is given by electron gain enthalpy.
Ex:-
It may be exothermic or endothermic
reaction.
·
Halogens show exothermic reaction &
have height – ve electron gain enthalpy.
·
Noble gases show endothermic reactions
& have lowest +ve electron gain enthalpy.
5. Electronegativity: -
The qualitative measure of ability of atom to attract shared electrons from chemical compound (or chemical bond) toward itself is known as electronegativity.
·
It generally decreases down in a group and
increases in a period from left to right.
Periodic trends in chemical properties:-
1. Trends in valence or oxidation states: -
The valance or oxidation state depends on outer most orbital elements electron and / or eight minus the no. of outermost electrons. |
| Periodic Table |
If you're ready to dive into the amazing world of elements, this book is a must-have. Packed with intriguing information and fascinating trivia, "Interesting Facts About All Elements of the Periodic Table" is waiting to inspire the next generation of scientists and satisfy the curiosity of today’s readers. Don’t miss your chance to own this unique book—get your copy today and embark on a journey that makes learning science fun!
Explore our Science Facts Book at
Amazon.com Book Store | Amazon.in Book Store | NotionPress Store | Author Page | Flipkart Book Store


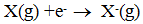




%20(1).png)
