Periodic Classification of Elements
In
year of 1800 about 30 elements were known but at present we know about 114
elements. All these elements have different properties. So, to study about these
elements easily, scientists start searching some patterns in the properties to
arrange these elements.
Early Attempts in the Classification of Elements
This
is practice to arrange elements in order out of chaos, means arranging elements
in group of metals and non-metals. Chaos means complete disorder or confusing.
Furthermore, attempts were made to achieve best classification of the elements.
Dobereiner’s Triads
A German chemist,
Johann Wolfgang Dobereiner in 1817 tried to arrange elements in the group of
3-elements in each group with similar properties and he called these groups as
‘Triads’. Dobereiner shows that when we take any triad and arrange its elements
in the order of increasing atomic masses then the atomic mass of the middle
element in the triad is roughly equal to the average of the 1st and
3rd element of the triad.
Dobereiner Triads
|
|
|
In
first triad Li, Na, K atomic mass of Na
(23) = [ Li(7) + K(39)]/2
Newlands Law of Octaves
An English
scientist, John Newlands in 1866 arranges known elements in order of their
increasing atomic masses. At that time he started with Hydrogen as 1st
element with lowest atomic mass and ended at Thorium as 56th
element. John Newlands observe that the
property of every eighth element is
similar to that of first element and compare this to octaves of music so he
called it ‘Law of Octaves’ and this is known as ‘Newlands Law of Octaves’.
Newlands Octaves
H
|
Li
|
Be
|
B
|
C
|
N
|
O
|
F
|
Na
|
Mg
|
Al
|
Si
|
P
|
S
|
Cl
|
K
|
Ca
|
Cr
|
Ti
|
Mn
|
Fe
|
Co
and Ni
|
Cu
|
Zn
|
Y
|
In
|
As
|
Se
|
Br
|
Rb
|
Sr
|
Ce
and La
|
Zr
|
-
|
-
|
1. Newlands law of octaves is applicable only up to Calcium and after Calcium it is not applicable because after Calcium every eighth element is do not similar to that of first element.
2. Newlands assumed only 56 elements exists in nature but later several elements discovered whose properties are very different to get fit in Newlands law of octaves.
3. With the discovery of new elements, Newlands try to fit these elements in octaves so he put two elements in same slot and Newland also put elements with different properties in same slot for example Co and Ni placed in F, Cl column.
Mendeleev’s Periodic Table
A Russian
chemist, Dmitri Ivonovich Mendeleev in 1872 published his ‘Mendeleev Periodic
Table’ in a German journal. He arranges
elements in the form of table on the basis of fundamental property of elements
i.e. atomic mass and also on the basis of similarity of chemical properties of
elements, means elements with similar chemical properties are placed together
in table.
Mendeleev Periodic Law
According to this
law “the properties of elements are the
periodic function of their atomic masses”.
In
Mendeleev periodic table horizontal rows are called as ‘Periods’ and vertical
columns are called as ‘Groups’.
Achievements of Mendeléev’s Periodic Table
Mendeléev’s
Periodic Table contains some gaps, but Mendeléev predicted that these gaps are
filled by elements discovered in future. And named these undiscovered elements
by placing eka (one) as a prefix to the name of preceding element of the same
group. For example, Gallium discovered later but Mandeleev predict it as
Eka-Aluminium.
Properties
of Eka-Aluminium and Gallium
Property
|
Eka-Aluminium
|
Gallium
|
Atomic Mass
|
65
|
69.7
|
Formula of Oxide
|
E2O3
|
Ga2O3
|
Formula of Chloride
|
ECl3
|
GaCl3
|
This
prediction of Mandeleev proves correctness and usefulness of Mendeléev’s
Periodic Table. Another achievement of Mandeleev is that many scientists now recognize
him as originator of the concept on which periodic table is based and also when
inert gases (means Nobel gases like He, Ne, Ar) are discovered, they are placed
in separate column without disturbing existing order of elements.
Limitation of Mandeleev Classification
These
given below are the limitation of Mandeleev Classification.
1. Position of Hydrogen- No fixed position given to Hydrogen as it behaves like both alkali metals and halogens. Like alkali, Hydrogen react with halogen oxygen and sulphur and also like halogen, Hydrogen exist in diatomic form and react with metals and non-metals.
2. Isotopes- Isotopes have similar chemical properties but different atomic masses, so Isotopes are challenge to Mandeleev Periodic Law.
3. Prediction of New Elements- Atomic masses of elements do not increase in regular manner so we cannot predict how many elements can be discovered between two elements.
1. Position of Hydrogen- No fixed position given to Hydrogen as it behaves like both alkali metals and halogens. Like alkali, Hydrogen react with halogen oxygen and sulphur and also like halogen, Hydrogen exist in diatomic form and react with metals and non-metals.
2. Isotopes- Isotopes have similar chemical properties but different atomic masses, so Isotopes are challenge to Mandeleev Periodic Law.
3. Prediction of New Elements- Atomic masses of elements do not increase in regular manner so we cannot predict how many elements can be discovered between two elements.
Modern
Periodic Table
Henry Moseley in
1913, after performing many experiments proves that atomic number is more
fundamental property than atomic mass of an element. So he prepare periodic
table on the basis of atomic number means elements are arranged in the order of
increasing atomic number in Modern Periodic Table.
Modern
Periodic Law
According to this
law “the properties of elements are the
periodic function of their atomic number”.
In
Modern Periodic Table limitation of Mandeleev Classification are removed.
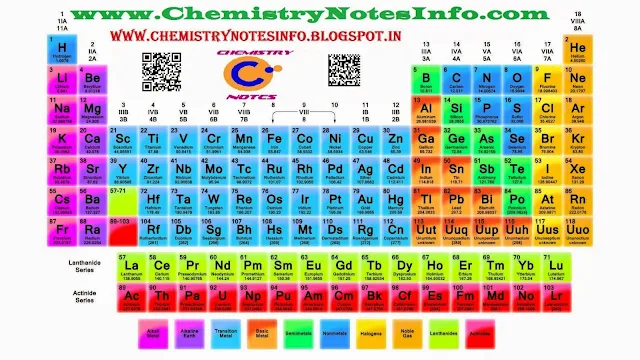
Modern Periodic Table
Position
of Elements in Modern Periodic Table
Modern
Periodic Table contains 18 vertical columns (means 18 Groups) and 7 horizontal
rows (means 7 Periods).
In Group-
Elements in a group have same number of valence electrons means identical
outershell electronic configuration, but as we move downside in a group number
of shells increases.
In Period-
Elements in a period have same number of shells. Also as we move from left to
right in a period, atomic number increases by one unit so number of valence
shell electrons also increases by one unit.
Trends
in the Modern Periodic Table
Valency
Number of valence electrons in outer
most shell of any atom is called valency of that atom. As we move from left to
right in a period, atomic number increases by one unit so valence electrons
also increases by one unit but in a group it remains constant.
Atomic
Size
Atomic size is determined by
atomic radius.
In
a Period- Atomic radius decreases as we move from left to right in a period,
because as we move from left to right in a period Nuclear Charge (+ve)
increases which pulls electrons (-ve) towards nucleus result in decreasing
atomic size or decrease atomic radius.
In
a Group- Atomic radius increases as we move from top to bottom in a group,
because new shells are added which increases distance between nucleus and
outermost electrons.
Metallic
and Non-metallic Properties
Elements
towards left hand side in periodic table are metals while elements towards
right hand side in periodic table are non-metals. Elements which separate
metals and non-metals have the properties of the both metals and non-metals are
known as Metalloids or Semi-Metals.
Example
of Metals- Na, Mg, Al, Fe
Example
of Non-metals- S, Cl, F, Br
Examples
of Metalloids or Semi-Metals- B, Si, Ge, As, Sb, Te, Po
In
a Period- Metallic character decreases and Non-metallic character increases as
we move from left to right in a period because tendency to lose valence
electrons decreases due to increasing
nuclear charge as we move from left to right in a period.
In
a Group- Metallic character increases and Non-metallic character decreases as
we move from top to bottom in a group because tendency to lose valence electrons
increases due to increasing valence shells (i.e. increasing distance between
nucleus and outermost electron) on moving from top to bottom in a group.
Metals
are electropositive as they forms bonds by loosing electrons while Nonmetals are
electronegative as they forms bonds by gaining electrons.
In
general cases, oxides of metals are basic in nature while oxides of non-metals
are acidic in nature.
If you're ready to dive into the amazing world of elements, this book is a must-have. Packed with intriguing information and fascinating trivia, "Interesting Facts About All Elements of the Periodic Table" is waiting to inspire the next generation of scientists and satisfy the curiosity of today’s readers. Don’t miss your chance to own this unique book—get your copy today and embark on a journey that makes learning science fun!
Explore our Science Facts Book at
If you're ready to dive into the amazing world of elements, this book is a must-have. Packed with intriguing information and fascinating trivia, "Interesting Facts About All Elements of the Periodic Table" is waiting to inspire the next generation of scientists and satisfy the curiosity of today’s readers. Don’t miss your chance to own this unique book—get your copy today and embark on a journey that makes learning science fun!
Explore our Science Facts Book at






%20(1).png)
