Metals and Non-Metals
Metals
Metals are the solid materials
which are typically hard, malleable, ductile and conduct heat and electricity,
and also possess metallic lusture.
Example- Iron, Gold,
Aluminium, Silver, Copper etc.
Nonmetals are chemical
elements which lacks metallic properties. Non metals are either solids or gases
except Bromine (Br2), which occurs as liquid. Non-metals vaporizes
easily, insulator of heat and electricity. Nonmetals have high ionization
energy and electronegativity values.
Example- Hydrogen, Helium,
Nitrogen, O2, F2, Ne, Cl, Ar, Kr, Xe, Rn, Br, C, P, S,
Se, I.
Exception in metals and non-metals
·
Mercury is liquid
at room temperature while other metals are solid.
·
Gallium and caesium
have very low M.P. while other metals have very high M.P.
·
Iodine is
non-metal but it has lustre (shiny).
·
Carbon
(Non-Metal) exist in different forms, and these forms are known as allotrope.
·
Graphite
(allotrope of carbon) conduct electricity and Diamond (allotrope of carbon)
having very high M.P. and B.P. is hardest natural substance known.
Chemical properties of metal
Burning of metals in air
Metals
burn in air (as oxygen present in air) to produce metal oxide.
Metal + Oxygen -------> Metal Oxide
Example- 2Cu (Copper) + O2
(air) ----> 2CuO (Copper Oxide)
4Al (Aluminium) + 3O2
--------> 2Al2O3
(Aluminium Oxide)
·
Mostly metal
oxide is basic in nature, but some metal oxides are amphoteric in nature i.e.
they show acidic as well as basic behaviour like Aluminium Oxide, Zinc Oxide.
Al2O3
+ 6HCl --------> 2AlCl3 + 3H2O
Al2O3 + 2NaOH -----> 2NaAlO2 (Sodium Aluminate) + H2O
·
Mostly metal
oxide does not dissolve in water but some dissolve to form alkali.
Na2O
(s) + H2O (l) ----------> 2NaOH (aq)
K2O
(s) + H2O (l) ---------> 2KOH (aq)
·
Some metals prevent
further corrosion by making protective oxide layer on itself like Al, Zn, Pb
etc.
·
Some metals like
Na, K catches accidental fire so to prevent it, they are kept fully immersed in
kerosene oil.
Reaction of metals with water
Most metal react with water to form metal oxide and hydrogen gas.
Metal + Water ------> Metal Oxide + Hydrogen Gas
2K (s) + H2O (l)
--------> K2O (s) +
H2 (g)
Not all, but some metal oxide
reacts further with water to give metal hydroxide.
K2O (s) + H2O
(l) ------> 2KOH (aq)
Some metals do not react with
water like copper, lead, silver and gold.
Reaction of metals with acids
Most metal react with acids to produce salt and hydrogen gas.
Metal + Diluted Acid ---------> Salt + Hydrogen Gas
2Al + 6HCl (dil.) ----------> 2AlCl3 + 3H2
·
As HNO3
is strong oxidizing agent so, hydrogen gas does not evolve when reaction take place
between metal and nitric acid Because HNO3 reduces itself to
nitrogen oxides (N2O, NO, and NO2).
·
Aqua-Regia (Royal
Water) is freshly prepared mixture of concentrated Hydrochloric Acid (Conc.
HCl) and concentrated Nitric Acid (Conc. HNO3) in the ratio of 3:1.
Aqua
Regia have great dissolving power, highly corrosive, fuming liquids. Aqua Regia
have ability to dissolve gold and platinum.
Reaction of metals with solution of other metal salts
More reactive metal has ability to displace less reactive metal from
their compounds in molten or solution form.
For example, if metal A is
more reactive then metal B then it displaces metal B from solution of metal B.
Metal A + Salt Solution of B
------> Salt Solution of A +
Metal B
Fe (s) + CuSO4 (aq)
-----> FeSO4 (aq)
+ Cu (s)
Reactivity Series of Metals
Reactivity series is the series in
which metals are arranged as per order of decreasing activity. This reactivity
series is developed after performing so many displacement experiments. This series
is also called as activity series.
K
|
Pottasium
|
More Reactive
Reactivity
Decreases
when we move Top to Bottom Least Reactive |
Na
|
Sodium
|
|
Ca
|
Calcium
|
|
Mg
|
||
Al
|
Aluminium
|
|
Zn
|
Zinc
|
|
Fe
|
Iron
|
|
Pb
|
Lead
|
|
H
|
||
Cu
|
Copper
|
|
Hg
|
Mercury
|
|
Ag
|
Silver
|
|
Au
|
gold
|
How Metals react with Non-metals
As
we know every element has tendency to achieve completely filled valence shell
to get electronic configuration of nearby noble gas, for example a metal says
sodium (Na) react with non-metal chlorine (Cl) to get complete valence shell
so Na loose one electron from its outermost shell which is taken-up by chlorine
(Cl), as a result they both have completely filled valence shell. In this
process sodium become +vely charged and chlorine –vely charged and these charges
attract each other to form NaCl.
Na (2,8,1) --------> Na+ (2,8) + e-
Where,
Na+ is sodium cation
Cl (2,8,7) + e- ----------> Cl-
Where,
Cl-
is chlorine anion
Formation of Sodium Chloride
Na+ + Cl- -----------> NaCl
Properties of Ionic Compounds
Ionic
Compounds also called Electrovalent Compounds and their properties are
described below-
1. Physical Nature of Ionic Compounds
Ionic compounds are solid and hard due to strong force
of attraction between +ve and –ve ions. Ionic compounds are also brittle.
2. Melting and Boiling Points of Ionic Compounds
Ionic Compounds have high M.P. and B.P. as large
amount of energy is needed to breakup ionic bonds.
3. Solubility of Ionic Compounds
Ionic compounds are soluble in polar solvents like
water and insoluble in non-polar solvents like ether, kerosene etc.
4. Electric Conductivity of Ionic Compounds
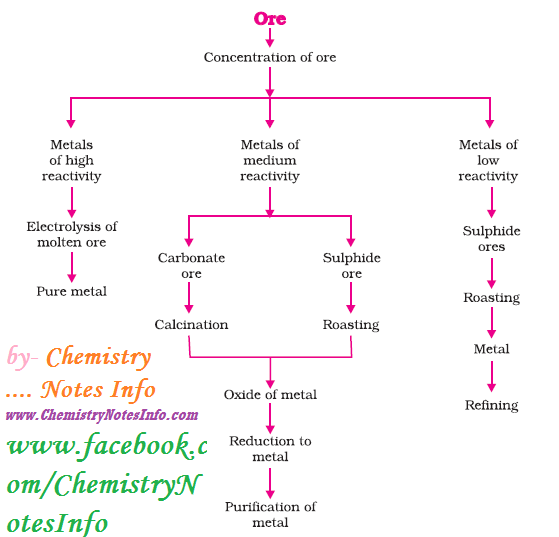
Occurrence of Metals
Maximum
metals occur in earth’s crust and some metal occur in sea water. Metals and its
compounds exist as minerals and if the percentages of metals in minerals are
large then they are known as ores.
1. Extraction of Metals
Reactivity series is very helpful in
metal extraction as metals present at the bottom of reactivity series are least
reactive so found in Free State like gold, silver and platinum found in Free-State.
Metal at top is most reactive and metals in the middle are also reactive so
found in combined form. Metals generally found as oxides, sulphides and
carbonates on earth’s crust.
Steps involved in extraction of metals from ores-
2. Enrichment of Ore
The process
of removal of impurities or gangue from ore, before extraction of metal is
known as enrichment of ore.
Gangue is terminology used for impurities like sand,
soil etc. present in ore.
3. Extracting Metals Low in Reactivity Series (or Activity Series)
Metals present at bottom (or low
position) in activity series are very unreactive and can be obtained in pure
metallic form by just heating alone.
Example- Cinnabar (HgS), ore of Mercury (Hg)
2HgS (s) + 3O2 (g) + heat ----------> 2HgO (s) + 2SO2 (g)
2HgO (s) + Heat ------------> 2Hg (l) + O2 (g)
Similarly,
Cu2S, ore of copper (Cu)
2Cu2S + 3O2 (g)
+ Heat ----------> 2Cu2O (s) + 2SO2 (g)
2Cu2O + Cu2S + Heat ----------> 6Cu (s) + SO2 (g)
4. Extracting Metals in Middle of Activity Series
Metals in
middle like iron, zinc, lead etc. are moderately reactive and present as
sulphides or carbonates. Metals can be easily extracted from its oxides so
sulphides and carbonates are reduced to oxides. Then these metal oxides are
reduced to corresponding metal by using suitable reducing agent like carbon. Chemistry Notes by Chemistry Notes Info.
Roasting
It
is a process of converting sulphide ores into oxides by heating strongly in the
presence of excess air.
2ZnS (s) + 3O2 (g) + Heat
---------> 2ZnO (s) + 2SO2
(g)
Calcination
It is a process of converting carbonates
ores into oxides by heating strongly in the presence of limited air.
ZnCO3 (s) + Heat ----------> ZnO (s) +CO2 (g)
Oxide Reduction
Oxides of ores are reduced to metal by
using suitable reducing agent like carbon (Coke), or highly reactive metals.
ZnO (s) + C (s) ---------> Zn (s) + CO (s)
3MnO2 (s) + Al (s) -----------> 3Mn (l) + Al2O3 (s) + Heat
5. Extracting Metals at Top of Activity Series
Metals present at top in
activity series are very reactive and they are not obtained by heating their
compounds with carbon, for example Sodium, Calcium, Magnesium, Aluminium etc.
cannot be obtained by reducing with carbon as these metals have more affinity
for oxygen than carbon. So these metals are obtained by electrolytic reduction.
In
electrolytic reduction, the metals get deposited at cathode (-ve electrode) and
gas like chlorine get liberated at anode (+ve electrode)
Reaction for molten Sodium Chloride-
At Cathode :-
Na+ + e- --------> Na
At Anode :-
2Cl- -------> Cl2 + 2e-
Refining of Metals
Refining of metals are done to obtain
metals in very pure form by removing impurities present in it. Electrolytic
refining is widely used method for this purpose.
Electrolytic Refining
Electrolytic
refining is the method of obtaining very pure metals from impure metal. Metals
like copper, zinc, nickel, silver, tin, gold etc. are refined electrolytically.
In electrolytic refining, anode (+ve) is made from
impure metal and cathode (-ve) is made from thin strip of pure metal. Metal
salt solution works as an electrolyte. When we applied electric current across
the electrodes then current starts flow through electrolytic solution. Pure
metal comes out from anode and dissolve in electrolyte and equivalent amount
(i.e. to that comes from anode) of this pure metal from electrolyte solution
get deposited on cathode.
“In simple way we can say that pure metal come from
anode and get deposited on cathode by using electrolyte solution and electric
current.”
Insoluble impurities settle down below anode at bottom
and we say it as anode mud, while soluble impurities mix in electrolyte.
Corrosion
Natural
process of conversion of refined metal to its high stable form like oxides or
hydroxides of metals is known as corrosion. Corrosion is the process of gradual
destruction of any material like metals by environment and chemical reaction.
Example - Rusting of Iron
Prevention of Corrosion
There
are so many methods to prevent corrosion like-
1. Applied Coating
Applied
coating is surface treatment method. Planting, enamel application and painting
are applied coating method to prevent corrosion. These methods create barrier
between metal and environment.
2. Anodization
It
is anode surface treatment process in which we made thicker oxide layer at
metal surface.
3. Galvanization
Galvanization
is the process of coating steel and iron with very thin layer of zinc to
protect them from rusting.
Overall painting, greasing, oiling, chrome plating,
galvanizing, alloy making and anodizing are some ways for the prevention of
corrosion.


%20(1).png)
